Bearded Dragons and Chameleons are two of the most popular types of lizards kept as pets. They both have their own unique features and appeal to different kinds of people. So, which one is right for you? In this comprehensive guide, we will compare and contrast these two amazing creatures, so that you can make an informed decision about which one is best for your family!
Bearded Dragon vs. Chameleon – Common Facts
Are you looking to buy a pet reptile, but can’t decide?
There are actually quite a few differences between these two reptiles that might help you make your decision. In this article, we’ll go over some of the key points to help you understand the bearded dragon vs. chameleon debate.
Bearded Dragons Common Form
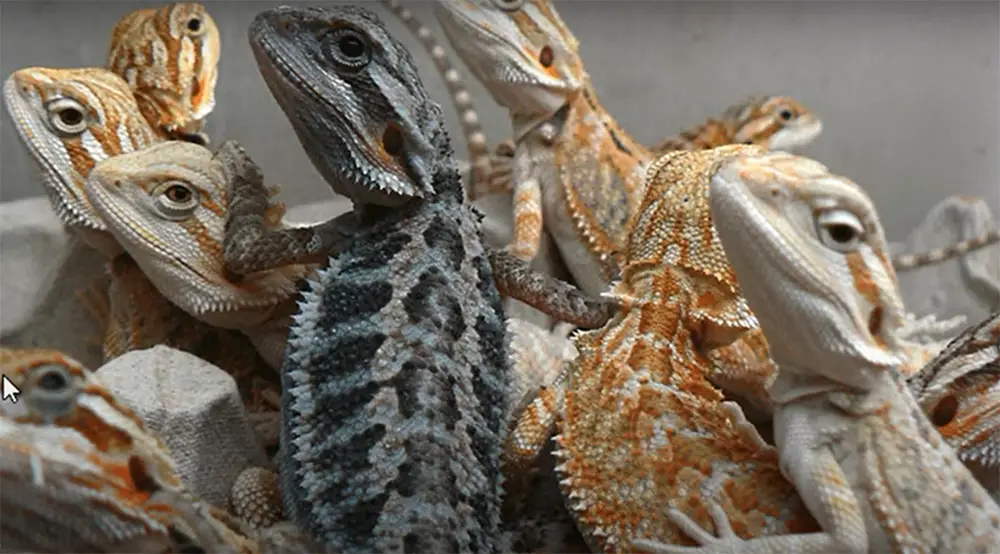

The bearded dragon is a type of lizard that can be kept as a pet. Male chuckwallas grow to around 20 inches long, whereas females reach a length of approximately 18 inches. They have a light brown body with dark bands running across their back and tail. Their belly is a creamy white color. [1]
Bearded Dragons Habitat
Bearded dragons are found in the dry, arid regions of Australia. They prefer areas with plenty of rocks and places to hide from predators.
Bearded Dragons Behavior
Bearded dragons are solitary animals and are only social when they are young. They become aggressive as adults and will fight with other bearded dragons if they are not given enough space. Bearded dragons are also known to be very active during the day and sleep at night.
Bearded Dragons Diet
Bearded dragons are omnivores, which means that they will eat both plants and animals. In the wild, their diet consists of about 80% plant matter and 20% insects. [2] The most common vegetables that they eat are leafy greens like collard greens, mustard greens, and turnip greens. They also enjoy eating fruits like figs, apricots, and grapes. As for insects, their favorites are crickets, mealworms, and wax worms.
In captivity, bearded dragons should have a diet that consists of about 50% vegetables and 50% insects. This can be accomplished by feeding them a variety of different vegetables as well as offering them live insects to eat.
Bearded dragons are prone to obesity, so it’s important to not overfeed them. A good rule of thumb is to offer them as much food as they can eat in one sitting and then remove any uneaten food.
Another thing to keep in mind is that bearded dragons need to have a calcium supplement added to their diet. This is because they are unable to synthesize calcium on their own. A good way to provide them with a calcium supplement is to dust their food with a powder that contains calcium.
Bearded Dragons Reproduction
Bearded dragons are Oviparous, which means they lay eggs. The female will lay a clutch of anywhere from 12 to 30 eggs in a nest that she has dug or in an artificial incubator. The eggs will hatch 60 to 80 days later.
Chameleons Common Form
The chameleon’s body is laterally compressed. This allows it to change its appearance by altering the skin’s texture and color. Chameleons can range in size from less than an inch to over two feet.
Chameleons Habitat
Chameleons are found in Africa, Madagascar, southern Europe, and across southern Asia as far as Sri Lanka. They mostly live in trees, but some will spend time on the ground or in bushes. [3]
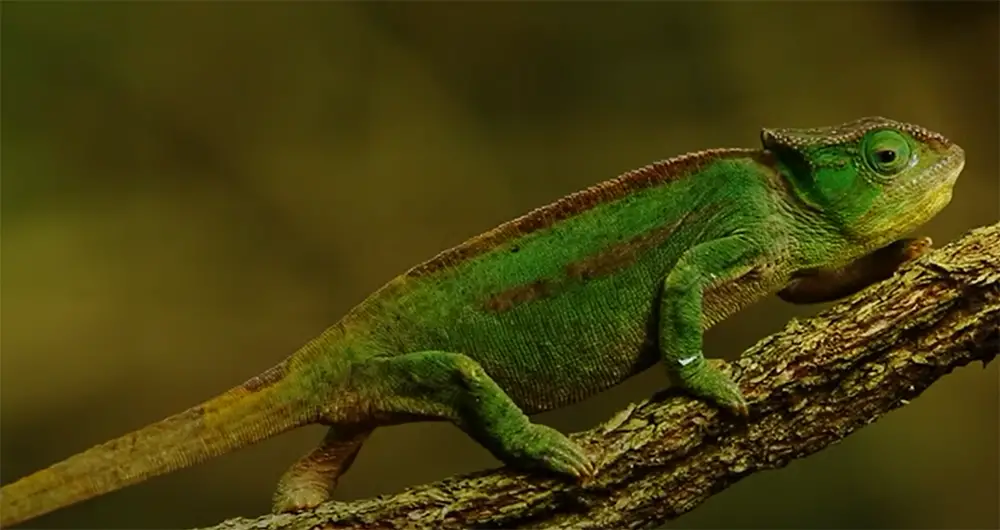

They are well-camouflaged creatures that rely on their color-changing ability to hide from predators and sneak up on prey.
Chameleons are usually green, but their color can range from brown to yellow to red, and they may even be striped or have spots.
There are more than 160 species of chameleon, and they come in a variety of sizes, with the smallest being about an inch long and the largest reaching up to two feet.
Chameleons Behavior
Chameleons are very shy animals. They will avoid contact with other chameleons and even humans. When they feel threatened, they will puff up their throat sacs and hiss. Chameleons are also known to be aggressive towards other chameleons and even humans.
They are generally solitary creatures, but they will come together to mate.
Males are often quite aggressive towards each other and will fight for the chance to mate with a female.
After mating, the female chameleon will lay her eggs in a hole that she digs in the ground.
Chameleons Diet
Chameleons are mostly insectivores, so their diet revolves around insects. In the wild, they will eat whatever insects they can find, including crickets, grasshoppers, moths, and flies.

Bearded dragons in the wild eat a mix of insects and plants. But in captivity, their diet is usually made up of commercial bearded dragon food, crickets, vegetables, and the occasional treat.
One big difference between the two is that chameleons need live prey. This means that their diet needs to be supplemented with live insects. Bearded dragons can eat both live and frozen/thawed prey.
Another big difference is that chameleons eat much smaller insects than bearded dragons. This is because their mouths are much smaller. So, if you’re feeding your chameleon crickets, you’ll need to make sure they’re small enough for them to eat.
Chameleons Reproduction
Chameleons are oviparous, which means they lay eggs. The female chameleon will usually lay 20 to 30 eggs at a time and will do so every few months. The incubation period for chameleon eggs is about two months.
Bearded Dragon vs. Chameleon – Common Disease
Bearded dragons and chameleons share some common diseases, but they also have a few that are unique to their species. Bearded dragons are susceptible to parasites, respiratory infections, and stomatitis. Chameleons, on the other hand, are more likely to get metabolic bone and infectious diseases.
Tail Loss
The tails of bearded dragons and chameleons are one of the most obvious distinctions between the two species. A chameleon will regularly shed its tail as a defense mechanism, while a bearded dragon will only lose its tail if it’s sick or under stress. If you’re looking for a non-dropping tail pet, a bearded dragon is the greatest option.
Bearded dragons are also better equipped to handle tail loss than chameleons. When a chameleon loses its tail, it’s permanently gone and the chameleon won’t be able to grow a new one. A bearded dragon, on the other hand, can regenerate its tail if it’s lost.
So, if you’re looking for a pet that won’t lose its tail at the first sign of trouble, a bearded dragon is the way to go. If your chameleon does happen to lose its tail, don’t worry – it will eventually grow back.
Thermal Burns
Bearded Dragons and Chameleons are both reptiles that come from warm climates. They both like it hot! But there is a big difference in the way they can tolerate heat. Bearded dragons come from the desert where temperatures can get up to 115 degrees Fahrenheit. They have adapted to be able to withstand these high temperatures by basking in the sun all day. Chameleons come from the tropical rainforest where temperatures are milder, around 80-85 degrees Fahrenheit. They have adapted to this climate by spending most of their time in the trees where it is cooler.
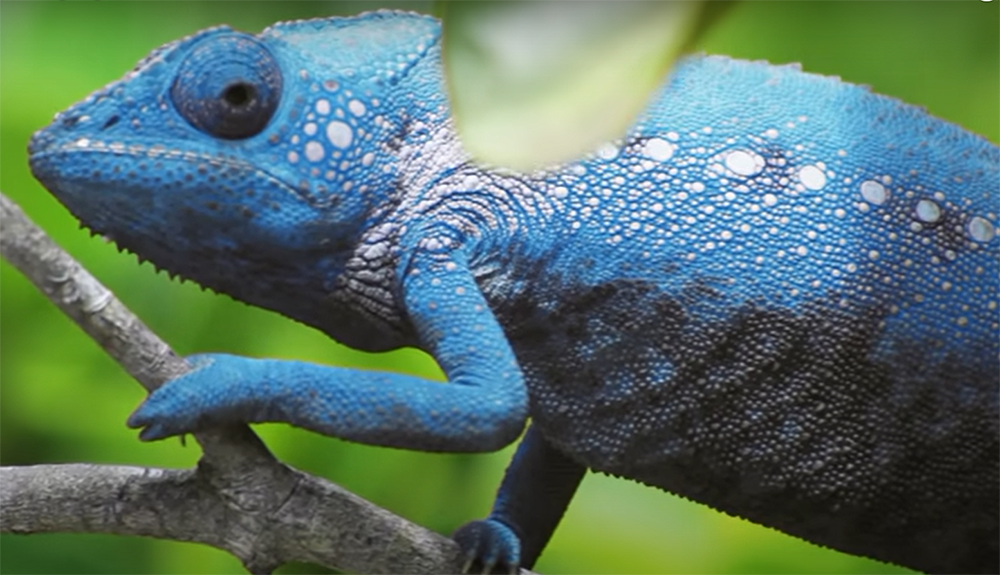

If you live in a hot climate, you will need to provide your Bearded Dragon with a basking spot that is around 110 degrees Fahrenheit. You can use a basking bulb or a ceramic heat emitter to create this spot.
Chameleons, on the other hand, should not be kept in an area that is too hot. If the temperature gets above 90 degrees Fahrenheit, they will start to experience thermal burns. These burns can be fatal, so it is critical to make sure your Chameleon’s enclosure is not too hot.
Dehydration
One of the main differences between bearded dragons and chameleons is that bearded dragons are much more susceptible to dehydration. This is due to the fact that they are desert dwelling animals and need to be able to conserve water. Chameleons, on the other hand, come from tropical rainforests where there is an abundance of water. As a result, they are not as susceptible to dehydration.
Dehydration can be deadly for bearded dragons. This is why it is so important to make sure that clean water is available to your bearded dragon at all times. If you are ever unsure if your bearded dragon is dehydrated, it is always best to err on the side of caution and take them to the vet.
Chameleons do not require as much water as bearded dragons. In fact, giving them too much water can actually be harmful. This is because chameleons absorb water through their skin and too much water can cause them too bloated and uncomfortable.
Lungs Issue
Bearded dragons have lungs that are more efficient at exchanging oxygen than those of chameleons. This gives them an advantage in hot, dry habitats where there is less oxygen in the air to breathe.
Chameleons have smaller, less efficient lungs that make them more dependent on humid environments where there is more oxygen available in the air.
Kidney Disease
One of the most common health problems in bearded dragons is kidney disease. This can be caused by a number of things, including dehydration, stress, and poor diet. Symptoms include weight loss, lethargy, and decreased appetite. If you think your dragon may have kidney disease, take them to the vet immediately.
Chameleons, on the other hand, are relatively resistant to kidney disease. This is due to their ability to store water in their bodies for long periods of time. However, chameleons can still suffer from dehydration if they do not have access to fresh water.
Bone Disease
There are several types of bone disease that can affect either bearded dragons or chameleons. Metabolic bone disease is the most common, and it occurs when there’s an imbalance in the calcium to phosphorus ratio in the reptile’s diet. This can lead to softening of the bones and deformities. Another type of bone disease, known as osteoporosis, can also occur if the reptile isn’t getting enough vitamin D.
Egg Binding

One of the most common problems faced by female bearded dragons is egg binding. This occurs when the female is unable to lay her eggs due to a blockage in the oviduct. The most common cause of this blockage is an infection, but it can also be caused by stress or dehydration. If your female bearded dragon shows any signs of egg binding, it is important to take her to the vet immediately.
Chameleons also lay eggs. If a female chameleon is having trouble laying her eggs, it is most likely due to dehydration. [4]
Comparing Bearded Dragons and Chameleons
There are a few key areas in which bearded dragons and chameleons differ. For one, bearded dragons are terrestrial animals, meaning they live on the ground, while chameleons are arboreal, meaning they live in trees. This is reflected in their different body types – bearded dragons have sturdier legs built for walking on the ground, while chameleons have prehensile tails and clawed toes that help them grip branches.
Size
This difference in size means that bearded dragons require a lot more food and space than chameleons. They also have a much higher metabolism, so they need to be fed more often.
Bearded dragons are also much stronger than chameleons and can easily injure them if they are not handled correctly. Chameleons are delicate creatures and should be treated with care.
Location
Bearded dragons come from Australia, and chameleons come from Africa and Madagascar.
Chameleons are found in tropical rainforests. They’re very good climbers and spend most of their time in trees.
Tail
Bearded dragons have long tails that they use for balance and to store fat reserves. Chameleons also have long tails, but theirs are much thinner and used primarily for balance.
One of the most notable differences between bearded dragons and chameleons is their tail shape. Bearded dragons have thick, broad tails that taper to a point. Chameleons have very thin tails that are almost whip-like in appearance.
Camouflage
One of the most noticeable differences between bearded dragons and chameleons is their appearance. Chameleons are masters of camouflage, thanks to their ability to change the color of their skin. This is an adaptation that helps them blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators.
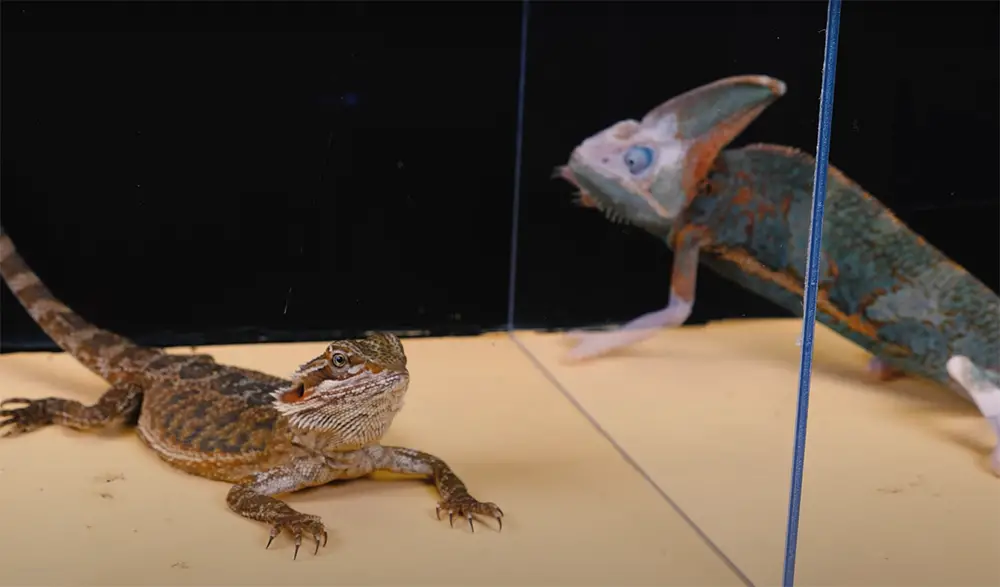

Bearded dragons have a more drab coloration, which helps them blend in with the desert environment where they live. While both reptiles can change their colors to some extent, chameleons are much better at it.
Eyes
The eyes of bearded dragons and chameleons are one of the most obvious distinctions. Bearded dragons have large, round eyes that are set far apart on either side of their head. This gives them excellent peripheral vision and allows them to see predators approaching from any direction. Chameleons have small, oval-shaped eyes that are located on either side of their head, but they can swivel independently to give them nearly 360-degree vision. This allows them to spot prey from any direction, as well as potential predators.
Life Expectancy
The average lifespan of a bearded dragon is between eight and twelve years, while the average lifespan of a chameleon is only four to eight years. This difference in life expectancy is due, in part, to the fact that bearded dragons are easier to care for than chameleons.
Diseases
Bearded dragons are susceptible to a number of diseases, including parasites, bacterial infections, and viral infections. Chameleons are not as prone to disease. However, they can still get sick if they are not properly cared for.
It is important to take your bearded dragon to the vet for regular check-ups to make sure they are healthy. If you think your bearded dragon is sick, take them to the vet right away.
Chameleons do not need to see the vet as often as bearded dragons. However, if you notice your chameleon is not acting like themselves, it is important to take them to the vet to get checked out.
Some common diseases that affect bearded dragons include:
- Parasites: Bearded dragons can get parasites from eating infected insects or from being in contact with an infected animal. Parasites can cause weight loss, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- Bacterial infections: Bacterial infections can cause respiratory problems, skin problems, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Viral infections: Viral infections can cause respiratory problems, paralysis, and death. [5]
Chameleons are not as susceptible to disease as bearded dragons. Some common diseases that affect chameleons include:
- Respiratory infections: Respiratory infections can cause difficulty breathing, wheezing, and coughing.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Gastrointestinal issues can cause vomiting and diarrhea.
- Paralysis: Paralysis can be caused by a number of things, including injuries and infections. [6]
The Cage Setup
Bearded dragons and chameleons have very different cage requirements. Bearded dragons are desert animals and need a hot, dry environment. Chameleons, on the other hand, come from tropical rainforests and need a humid environment.
There are a few key things to keep in mind when setting up a bearded dragon cage:
- The cage should be at least 20 gallons for a juvenile bearded dragon and 40 gallons for an adult.
- The cage should have a basking spot that is around 95 degrees Fahrenheit.
- The cage should have a cool side that is around 75 degrees Fahrenheit.
- The cage should be equipped with a UVB light to help the bearded dragon absorb calcium.
There are a few key things to keep in mind when setting up a chameleon cage:
- The cage should be tall rather than wide.
- The cage should have plenty of foliage for the chameleon to climb and hide.
- The cage should have a humidifier to maintain the humidity level.
- The cage should be equipped with a UVB light to help the chameleon absorb calcium.
Purchase cost
Bearded dragons cost between $40 to $150. Chameleons typically cost between $50 to $350, with veiled chameleons costing on the higher end.
Geographic location is also a factor in purchase cost. If you live in an area where reptiles are not common, you may have to pay more to have a specialty store import your animal.

Lifetime Maintenance cost
The bearded dragon has a lifespan of about 12-15 years in captivity, while the chameleon is only about half that. Chameleons also require more specialized care, which can drive up their lifetime maintenance cost.
FAQ
Is It Cruel To Own A Reptile As A Pet?
No, it is not cruel to own a reptile as a pet. In fact, reptiles can make great pets for people of all ages and lifestyles. Reptiles are low-maintenance pets that do not require much care or attention. They are also relatively inexpensive to purchase and maintain.
Which Is Better, Chameleon or Bearded Dragon?
Both lizards make great pets, but which is the better choice for you? In this article, we compare the two species side-by-side to help you make a decision.
Is It Better To Get A Female Or Male Chameleon?
It depends on what you’re looking for in a pet.
If you want a chameleon that is more likely to be docile and calm, then you should get a female. Female chameleons are typically less aggressive than males and are more likely to be content sitting in one place.
However, if you’re looking for a chameleon that is more active and playful, then you should get a male. Male chameleons tend to be more energetic and curious than females, making them more fun to watch.
Is It Better To Get A Female Or Male Bearded Dragon?
Male bearded dragons tend to be more territorial than females. This means that if you have multiple pets, a male bearded dragon might not do well with them. On the other hand, females are often more easy-going and can get along with other pets better.
Another thing to consider is that males tend to be larger than females. If you’re looking for a smaller pet, then a female might be a better option.
Can You Put A Chameleon And A Bearded Dragon Together?
The quick answer is no, you should not put a chameleon and a bearded dragon together. Although they may look similar, these two reptiles have different care requirements, and putting them together can stress or even injure both animals.
Is a bearded dragon easier to care for than a chameleon?
Bearded dragons are easier to care for than chameleons on the whole. They are less delicate, and can better tolerate a wider range of temperatures and humidity levels. However, this does not mean that they do not require special care.
Do Beardies bite?
Bearded dragons are not typically aggressive and will seldom bite. However, if they feel threatened or are mishandled, they may lash out and bite. If you have a Beardie that bites frequently, it could be a sign that something is wrong. [7]
Do bearded dragons stink?
Bearded dragons don’t typically stink. If your bearded dragon smells bad, it could be a sign of an infection or other health issue and you should take them to the vet.
Useful Video: Chameleons vs Bearded Dragon | Temperament – Very Basic Care
Conclusion
Overall, bearded dragons make great pets. They are low-maintenance, can be handled frequently, and have a docile personality. If you’re looking for a pet reptile that is easy to care for, a bearded dragon is a great choice. However, if you’re looking for a more unique reptile pet with interesting colors and patterns, a chameleon might be a better fit for you. No matter which reptile you choose, be sure to do your research so that you can provide the best care possible for your new pet. Thanks for reading!
References:
- https://petkeen.com/bearded-dragons-size-growth-chart/
- https://dragonsdiet.com/blogs/dragon-care/the-complete-bearded-dragon-diet-plan
- https://animalia.bio/common-chameleon
- https://www.chameleonschool.com/chameleon-eggs/
- https://reptile.guide/bearded-dragon-health-issues/
- https://animals.mom.com/common-illnesses-chameleons-2300.html
- https://totalbeardeddragon.com/do-bearded-dragons-bite/





Leave a Review